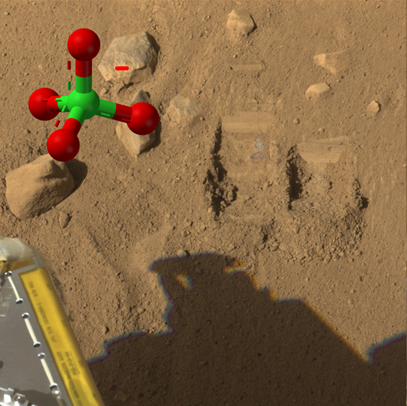
The primary objective of this project is to unravel the chemical and physical processes associated with the destruction of organics under simulated Mars surface conditions in the presence of perchlorates. In order to fully explore the destruction of organics, we have first systematically studied the energetic decomposition of pure perchlorates such as magnesium perchlorate hexahydrate Mg(ClO4)2∙6H2O at Mars relevant temperatures in order to trace the chemistry and source of reactive species. Magnesium perchlorate was chosen for this study as it has been suggested to be the most likely form of perchlorate in Martian regolith. Following the destruction of perchlorates, we explored the catalytic formation of perchlorates on the Martian surface via Galactic Cosmic Rays via modeling. Thereafter, we systematically explored the radiolytic destruction of key representative of amino acids and RNA nitrogen bases [glycine, adenine] of the pure compounds and in the presence of magnesium perchlorate with the former serving as the baseline for comparison with homogenous mixtures of the organics with magnesium perchlorate.



Recent Selected Publications
1. Y.S. Kim, K.P. Wo, S. Maity, S.K. Atreya, and R.I. Kaiser, Radiation-Induced Formation of Chlorine Oxides and Their Potential Role in the Origin of Martian Perchlorates, JACS, 135, 4910-4913 (2013). (PDF)
2. A.M. Turner, M.J. Abplanalp, R.I. Kaiser, Mechanistic Studies on the Radiolytic Decomposition of Perchlorates on the Martian Surface, Ap. J. 820, 127 (2016). (PDF)
3. S. Góbi, M.J. Abplanalp, R.I. Kaiser, Effect of Perchlorates on Electron Radiolysis of Glycine with Application to Mars, Ap. J. 822, 8 (2016). (PDF)
4. E.H. Wilson, S.K. Atreya, R.I. Kaiser, Perchlorate Formation on Mars through Surface Radiolysis Initiated Atmospheric Chemistry : A Potential Mechanism, Journal of Geophysical Research – Planets, 121, 1472-1487 (2016). (PDF)
5. S. Góbi, A. Bergantini, R. I. Kaiser, In Situ Detection of Chlorine Dioxide (ClO2) in the Radiolysis of Perchlorates and Implications for the Stability of Organics on Mars, Ap. J., 832, 164 (2016). (PDF)
6. S. Góbi, M. Förstel, P. Maksyutenko, R.I. Kaiser, A Reflectron Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometric Study on the Degradation Pathways of Glycine on Mars in the Presence of Perchlorates and Ionizing Radiation, Ap. J., 835, 241 (2017). (PDF)
7. S. Góbi, A. Bergantini, R.I. Kaiser, Degradation of Adenine on the Martian Surface in the Presence of Perchlorates and Ionizing Radiation: A Reflectron Time-of-flight Mass Spectrometric Study, J. ApJ, 838, 84 (2017). (PDF)
8. P.B. Crandall, S. Góbi, J. Gillis-Davis, R.I. Kaiser, Can perchlorates be transformed to hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) products by cosmic rays on the Martian surface?, J. Geophys. Res. Planets, 122, 1880-1892 (2017). (PDF)


